Did you study electromagnetism in school?
If you did, you might agree with me that school electromagnetism is chaos.
A plethora of formulas, incomprehensible phenomena, and the ultimately mysterious electric and magnetic fields leave many people's heads spinning.
However, true electromagnetism is a very elegant field where just four simple equations (Maxwell's equations) can explain all phenomena.
These four equations themselves go beyond the school curriculum, but their content is quite simple.
From here, I hope to help you intuitively understand electromagnetism from its fundamentals!
Electric Charge
The foundation of understanding electromagnetism is this electric charge .
This can be easily understood by comparing it to universal gravitation.
All objects with mass (weight) experience a force calleduniversal gravitation and attract each other.
The most familiar example is gravity. Gravity is based on the universal gravitation between the Earth and us.
Similarly, objects with electric charge experience a force called electromagnetic force.
For example, objects with positive and negative charges attract each other, while two objects with positive charges repel each other.
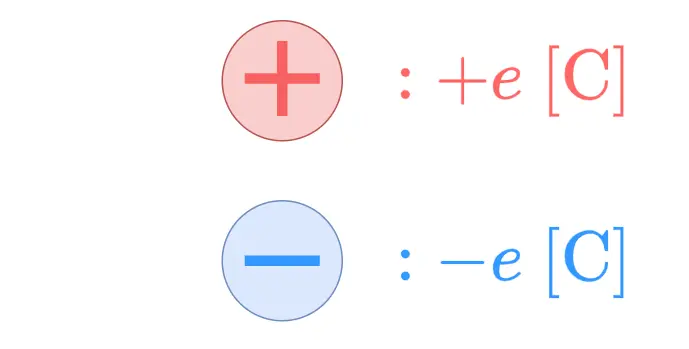
Typical examples of objects with electric charge are protons and electrons. They have charges of respectively. is called the elementary charge, and its value is .
.9160fd30.svg)
Unlike mass, which is always positive, electric charges can also be negative. (If you ever find an object with negative mass, let me know!)
Moreover, while mass is only affected by universal gravitation, electric charges experience a variety of forces, such as Coulomb force and electromagnetic force. These forces are collectively known as electromagnetic force.
Electric charge is the cornerstone of electromagnetism! From here, we'll explore how forces act on electric charges.
Electromagnetic Field
Both universal gravitation and electromagnetic force involve forces acting between objects at a distance. Doesn't that seem a bit strange?
In everyday life, it feels like you need to touch something to apply force to it.
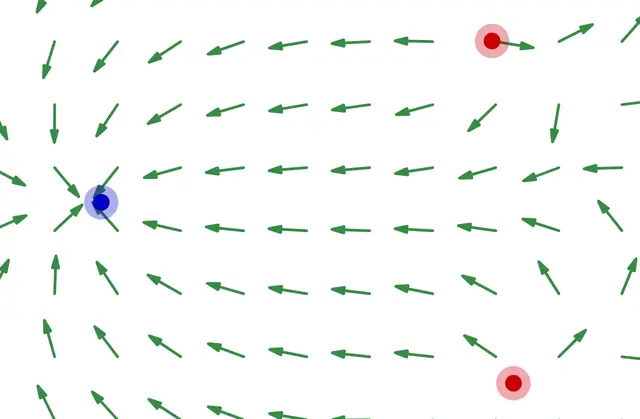
In reality, electric charges don't directly exert force on other charges at a distance. Instead, they first change the surrounding space, and this altered space then exerts force on other charges.
Changing space? What does that even mean? Before diving into that, let's first understand the concept of a "field," which is crucial in physics!
What is a Field?
Just as objects can have values like mass or density, every point in space can have various values.This is called a field.
At first, the concept of a field might not feel intuitive, but you are already using fields in your daily life. As we will explain later, light and radio waves are actually fields! Specifically, they are electric and magnetic fields, which we will deal with from now on.
Electric and Magnetic Fields
Among fields, those that can exert force on electric charges are calledelectric and magnetic fields!
.3c760765.svg)
As shown in this diagram, every point in space has two vector quantities called electric and magnetic fields.
In contrast, values with only magnitude are called scalar quantities.
When an electric charge exists at a certain point, it experiences a force according to the values of the electric and magnetic fields at that point. In other words, if you know the values of the electric and magnetic fields, you can determine the force acting on the charge and thus understand its motion!
By the way, the combination of electric and magnetic fields is called the electromagnetic field.
Relationship Between Electric Charge and Electromagnetic Field
Earlier, we mentioned that electric charges do not directly exert force on other charges at a distance. Instead, they first alter the surrounding space, and this altered space exerts force on other charges. This altered space is precisely the state in which an electromagnetic field is generated!
In other words, electric charges first create an electromagnetic field in the surrounding space. Then, this electromagnetic field exerts force on other charges!

Thus, the basics of electromagnetism are:
Key Points of Electromagnetism
- How electric and magnetic fields exert force on charges
- How electric and magnetic fields are generated
These two points!
Next, let's learn about how electric and magnetic fields exert force on charges!